Cysts of the Jaw
In This Article, we explain the definition of Cysts, its appearance radiologically, etiology, general classification and types.
Definition
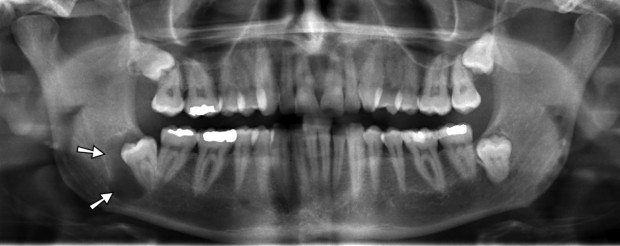
Radiology of the cysts
- Classically cyst appears as a well defined radiolucent area circumscribed by a radiopaque margin.
- Most cysts are unilocular , however keratocyst usually has a multilocular appearance.
- Cysts usually do not cause resorption of the roots of teeth, but it causes displacement.
Etiology
- The stimulus that causes resting epithelial cells to proliferate forming cyst is not exactly known .
- Inflammation seems to play a major role in those cysts arising in granuloma from infected dental pulp.
Classificaition
This Classification is the proposed revision of WHO Jaw Cyst Classification.
Developmental
- Odontogenic
- Odontogentic Keratocysts (Primodial Cyst).
- Follicular Cyst (Eruption Cyst).
- Alveolar Cyst of infants (Gingival Cyst in Adults).
- Developmental / Lateral Periodontal Cyst.
- Non-Odontogenic
- Midpalatal cyst of infants.
- Nasopalatine duct cyst.
- Nasolabial cyst.
Inflammatory
- Inflammatory follicular cyst.
- Radicular cyst.
- Inflammatory lateral periodontal cyst
Types of Cysts
cysts can be divided into three types according the its epithelium origin:
- Odontogenic epithelim: Epithelium responsible for tooth formation, read more.
- Non-odontogenic epithelium: oral epithelium entrapped along lines of fusion of the embryonic processes to form jaws, read more.
- Pseudocysts: Differ from true cyst in that they lack an epithelium lining , read more.
Diffrences
Difference between True Cyst and Pseudo-cyst can be explained by Dr. Varun Pandula from Juniour Dentist:
Cysts are Pathological cavities that contains (fluid, semi Fluid or gas) which is either lined by epithelium (True Cyst) or not lined by Epithelium (Pseudo-cyst).
Difference between a Cyst and Neoplasm
Cyst
- Sac filled with fluids or gas
- Will usually feel soft.
- Will usually feel soft.
- Lining by epithelium.
- Painless.
- Slow growing.
- Mainly benign.
- Rarely cause resorption of adjacent tooth but mainly causes displacement.
Neoplasm
- Solid Mass of tissues.
- Often Hard.
- May appear as a thin layer of flattened stratified squamous epithelium like.
- Tend to be painful.
- Rapidly growing.
- Either benign or malignant.
- Causes resorption of adjacent teeth.
Common Type
- Follicular ( dentigeorus ) cyst.
- Nasopalatine cyst.
- Radicular cyst.
- Keratocyst.
In The Next part of Cysts of the Jaw, we will explain about Odontogenic Cysts.
OziDent Members Only
The rest of article is viewable only to site members,Please Register and/ or Confirm registration via EmailHere.If you are an existing user, please login.